Three months before school. Tasks for the development of cognitive abilities (5-6 years). Kholodova O.A.

M.: 2009 - 80 p.
The manual is a collection of tasks for working with children on the eve of entering school. The tasks presented in this collection are so exciting that the child does not have to be forced to study. Completing these tasks will not only help the future first grader develop memory, attention, perception, thinking, form correct speech, improve graphic skills, but also provide the necessary base level knowledge, skills and abilities that will help him in the future to study well and easily at school. The manual is intended for classes with children 5-6 years old and is addressed to educators preparatory groups preschool institutions, teachers of gymnasiums, parents, as well as everyone who is interested in the successful preparation of the child for admission to grade 1.
Format: pdf
The size: 14 MB
Watch, download:drive.google
Going to school is an important moment in a child's life. Ahead is a new life, new friends, new, sometimes very serious trials. How to help a child quickly adapt to school, develop an interest in learning?
You want your child to study well, and at the same time be cheerful, cheerful and healthy. - help him. Good preschool- a guarantee of excellent studies at school.
To help prepare for school is the main objective of this manual.
With the help of a systematic approach adopted in the manual, it is possible to quickly and effectively develop in a preschooler such qualities as memory, attention, logical thinking, imagination, creative and spatial thinking, resourcefulness and ingenuity.
This manual offers various tasks that will teach children:
- listen, observe
- memorize and process the received information;
- identify different and identical properties of objects;
- recognize objects by given signs; describe objects;
- compare objects with each other;
- determine the sequence of events;
- navigate in space;
- generalize;
- classify;
- work according to the model;
- act in accordance with the accepted intention;
- Develop hand dexterity and mobility.
there are 36 lessons in the manual, which can be held either once a week from September to May (as a special course on the development of the cognitive abilities of a preschooler), or 3 times a week from January to April (as a preparation for a psychological and pedagogical interview when enrolling in grade 1 ), or 3 times a week from June to September (to develop children's skills, develop new skills, improve school readiness). Work with a child on the allowance should be dynamic, but not tedious, lasting no more than 30 minutes.
In the manual, the tasks follow each other in a certain order.
ANSWER determines the child's ability to quickly answer questions, assesses the level of general knowledge, horizons.
PERFORMANCE will help to evaluate the level of development of attention, memory, to understand how the child has developed logic, abstract thinking, to determine the level of the child's vocabulary.
DRAWING is aimed at developing motor skills, as well as the ability to perceive material by ear, reflect what is heard graphically, determines the child's readiness to write from dictation.
Instructions for working with these manuals are given on the back cover.
I wish you success in preparing your child for such an important, difficult, but wonderful and interesting period in life - for schooling!
cognitive interest attention logical thinking
In order for cognitive interest to be constantly reinforced, to receive impulses for development, it is necessary to use means that arouse in the student a feeling, a consciousness of his own growth. Make an answer plan, ask a friend a question, analyze the answer and evaluate it, summarize what has been said, look for a different way to solve the problem - these and many other methods that encourage the student to comprehend his activity steadily lead to the formation of a persistent cognitive interest.
Development of cognitive abilities
In the process of educational activity of a schoolchild, an important role, as psychologists note, is played by the level of development of cognitive processes: attention, perception, observation, imagination, memory, thinking. The development and improvement of cognitive processes will be more effective with purposeful work in this direction, which will entail the expansion of the cognitive capabilities of children. Attention is a form of organization of cognitive activity largely depends on the degree of formation of such a cognitive process as attention.
V educational material you can include content-logical tasks aimed at developing various characteristics of attention: its volume, stability, the ability to switch attention from one subject to another, distribute it to various items and types of activities.
- 1. Finding moves in ordinary and numerical mazes
- 2. Recalculation of objects depicted by repeatedly intersecting contours
- 3. Finding numbers from Schulte tables
- 4. Draw faster
- 5. Find out who is hiding
- 6. Find similarities and differences
- 7. Read the scattered words
Tasks aimed at developing perception and imagination. Perception is the main cognitive process of sensory reflection of reality, its objects and phenomena with their direct action on the sense organs. It is the basis of thinking and practical activity of both an adult and a child, the basis of a person's orientation in the world around him, in society. Psychological research has shown that one of effective methods organization of perception and education of observation is a comparison. Perception thus becomes deeper. As a result of playing and learning activities, perception itself turns into an independent activity, into observation.
- 1. Match the patch to the boot
- 2. Collect broken jug, vase, cups, plates
- 3. Exercise Geometric Shapes
- 4. Exercise Triangles
- 5. 100-cell table with graphic images
- 6. Table with geometric shapes of various shapes
- 7. Table with geometric shapes of different sizes
- 8. A table with geometric shapes not only of different shapes, but also in white and black
- 9. 100 cell table filled with numbers
Tasks aimed at developing logical thinking
Human intelligence. First of all, it is determined not by the amount of knowledge accumulated by him, but by a high level of logical thinking. Therefore, already in primary school it is necessary to teach children to analyze, compare and generalize information obtained as a result of interaction with objects not only of reality, but also of the abstract world. Nothing like mathematics contributes to the development of thinking, especially logical thinking, since the subject of its study is abstract concepts and patterns, which, in turn, are dealt with by mathematical logic.
- 1. Tasks for ingenuity
- 2. Tasks of the joke
- 3. Number shapes
- 4. Problems with geometric content
- 5. Logic exercises with words
- 6. Math Games and tricks
- 7. Crosswords and puzzles
- 8. Combinatorial problems
Tasks aimed at the development of memory. Memory is one of the basic properties of personality. The ancient Greeks considered the goddess of memory Mnemosyne the mother of the nine muses, patrons of all known sciences and arts. A man deprived of memory, in fact, ceases to be a man. Many outstanding personalities had a phenomenal memory. For example, Academician A.F. Ioffe used the table of logarithms from memory. But you should also be aware that good memory does not always guarantee its owner a good intellect. Psychologist T. Ribot described a weak-minded boy who could easily memorize series of numbers. And yet memory is one of the necessary conditions for the development of intellectual abilities. Primary schoolchildren have a more developed visual memory than semantic memory. They better remember specific objects, faces, facts, colors, events. But in elementary school, it is necessary to prepare children for secondary education, so it is necessary to develop logical memory. Students have to memorize definitions, proofs, explanations. By teaching children to memorize logically connected meanings, we contribute to the development of their thinking.
- 1. Remember two-digit numbers.
- 2. Remember math terms.
- 3. Chain of words.
- 4. Draw patterns from memory.
- 5. Remember and reproduce drawings
- 6. Visual dictations
- 7. Auditory dictations
Warm-ups
This technique of frontal work, involving the whole class in the activity, develops the speed of reaction, the ability to listen and hear the question, to think clearly and concretely. Interestingly, in this case, even those children who are usually silent, because they are intellectually passive or shy of public responses, work. The warm-up takes 5-7 minutes. What is the purpose of this type of work? It is carried out either at the stage of checking homework or primary assimilation, when the questions are very simple (reproductive) and require an unambiguous, quick answer that tests the knowledge and attention of children, the ability to listen and hear the question. If the oral warm-up is carried out at the beginning of the lesson before the explanation new topic, then it should include not only questions for checking homework, but also updating the basic concepts that were covered earlier (a week, a month, a year ago), which must be restored in the child's memory. Children are invited to answer questions in chorus as quickly as possible (usually 15-20 of them) and independently evaluate themselves: if the answer is correct, put a note in their notebook. At the end of the warm-up, the teacher explains how many answers you can put yourself "+".
Sections: Working with preschoolers
GOALS:
- Development of attention, memory, thinking.
- Preparing the hand to master writing.
Task 1. Warm-up
Answer the following questions as soon as possible:
- days in a week?
- toes?
- rear and front legs of a duck?
- seasons?
- winter months?
- gnomes at Snow White?
- human eyes and eyebrows?
- corners at the table, and if one was sawn off, how many are left?
Task 2. To complete the task, you will need subject pictures.
a) Name the objects in one word:
- goat, horse, cow, sheep (animals);
- teapot, plate, saucepan, glass (tableware);
- maple, birch, poplar, willow (trees).
b) Find the extra item and explain why it is superfluous:
- table, cabinet, Door, chair;
- spruce, oak, pine, stump;
- catfish, perch, pike, frog.
Task 3. Look closely and draw the missing figures in the empty squares.
Task 4. Find the differences in the pictures.

Physical education: The game "Flies, does not fly."
Attention! Now we will find out who can fly and who cannot. I will ask, and you immediately, without pauses, answer. If I call someone or something that can fly, for example, a dragonfly, answer “Flies” - and show how she does it, spreading her arms to the sides like wings. If I ask you: "Does the pig fly?" - be silent and do not raise your hands.
- Is the eagle flying?
- Does the sparrow fly?
- Is the cow flying?
- Is the snake flying?
- Is the kite flying?
- Does the helicopter fly?
Task 5. Who is lucky?

Task 6. Look carefully, remember and draw (cherries).
Task 7. Logic puzzle.
The flower does not grow under the tree.
A fungus does not grow under a birch,
What grows under the tree
what about under the birch.
Task 8. Draw straight lines along the dotted lines from left to right.

The manual is a collection of tasks for working with children on the eve of entering school. The tasks presented in this collection are so exciting that the child does not have to be forced to study. Completing these tasks will not only help the future first grader develop memory, attention, perception, thinking, form correct speech, improve graphic skills, but also provide the necessary basic level of knowledge, skills and abilities that will help him to study well and easily at school in the future.
The manual is intended for classes with children 5-6 years old and is addressed to teachers of preparatory groups of preschool institutions, teachers of gymnasiums, parents, as well as everyone who is interested in successfully preparing a child for admission to grade 1.
WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW AND KNOW A CHILD GOING TO SCHOOL.
1. Your first name, patronymic and last name.
2. Your age (date and year of birth).
3. Your home address.
4. Country and city in which he lives.
5. Surname, name, patronymic of parents, their profession.
6. Seasons (sequence, months, main signs of each season).
7. Part of the day (sequence, main features of each time of day).
8. Domestic animals, their cubs, habits.
9. Wild animals of our forests, hot countries, the North, their cubs, habits.
10. Wintering and migratory birds.
11. Transport ground, underground, water, underwater, air.
12. Distinguish between clothes, shoes and hats.
13. Distinguish vegetables, fruits and berries.
14. Freely navigate on a sheet of paper (right - left side, top - bottom).
15. Distinguish and correctly name planar geometric figures: circle, square, rectangle, triangle, oval.
16. Freely count from 1 to 10 and back.
17. Perform counting operations within 10 (+, 1, 2).
18. Distinguish between vowels and consonants.
19. Divide words into syllables with claps, steps, and so on.
20. Determine the number and sequence of sounds in words like "poppy", "house", "oaks", "sleigh", "wasps".
21. Know and be able to tell Russian folk tales.
22. Know by heart poems for children.
23. Be able to fully and consistently retell the listened story.
24. Be able to compose (invent) a story from a picture, from a series of pictures.
25. Handle a pencil: draw vertical and horizontal lines without a ruler, draw geometric shapes, animals, people, various objects based on geometric shapes, carefully paint over, hatch with a pencil without going beyond the contours of objects.
26. Use scissors well (cut strips, squares, circles, rectangles, triangles, cut an object along the contour).
27. Be able to perform the task according to the model.
28. Be able to listen carefully, without being distracted (20-30 minutes).
29. Remember and name 6-10 objects, pictures, words.
30. Maintain good posture when sitting.
Free download e-book in a convenient format, watch and read:
Download the book Three months before school, Assignments for the development of cognitive abilities, (5-6 years old), Workbook, Kholodova O., 2009 - fileskachat.com, fast and free download.
Download pdf
You can buy this book below best price at a discount with delivery throughout Russia.
Games for the development of cognitive processes in older children preschool age.
Shchipitsina Marina Ivanovna, educational psychologist, MBDOU "Savinsky Kindergarten”, the village of Savino, Perm Territory, Karagay District.Material Description: I bring to your attention games for the development of cognitive processes in children of preschool age. As a rule, the successful education of children in primary school depends on the level of development of cognitive processes. The material will be useful to parents and teachers, will help prepare children for school.
Successful education of children in primary school depends on the level of development of cognitive processes (thinking, speech, attention, memory, etc.), creatively solve various problems.
Preschool age is the period when the main activity of the baby is the game. In the game, it is easier to assimilate knowledge, skill, skills, with the help of game situation it is easier to attract the attention of the child, he remembers the material better, so try to choose tasks that are entertaining.
Remember that at this age, the duration of the lesson should not exceed 25 - 30 minutes. Don't let your baby get overwhelmed. I offer you several games that will help develop the cognitive processes of children:
Game "Superfluous word"
Purpose: development of thinking
Instruction: I will name 4 words, three of which can be combined, but one word does not fit them, it is superfluous.
For instance:
1. Book, TV, radio, tape recorder.
2. Russia, Poland, Moscow, Japan.
3. Dove, crow, bird, magpie.
4. Monday, Friday, May, Wednesday.
5. Sveta, Katya, Maltsev, Oleg.
Exercise "Semantic rows"
Purpose: development of thinking
Instruction: I'll give you three words, and you guess what the fourth one will be.
1. nest bird, dog - ...
2. jacket-fabric, boots-…
3. horse-foal, cow-…
4. book cover, house - ...
5. dog - puppy, man - ...
6. porridge-spoon, meat-…
7. boat-water, train-…
8. squirrel-hollow, man - ...
9. flower-stem, tree-…
10. window-sill, closet - ...
11. birch-leaves, pine - ...
12. the sun is light, the night is ...
13. button coat, boot - ...
Game "Continue the list of words"
Purpose: development of cognitive processes (attention, thinking, speech).
Instruction: continue the list of words and name the group with one word.
Russia, Poland… - doctor, teacher…
- Sveta, Natasha ... - Volga, Kama ...
- boots, shoes ... - birch, poplar ...
- titmouse, dove ... - hare, bear ...
- tulip, carnation ... - skates, skis ...
- March, January ... - nest, hole ...
- blue, red ... - raspberries, currants
- one, two ... - Venus, Jupiter ...
- rain, hail ... - sneakers, shoes ...
- sour cream, kefir ... - cake, cake ...
- minute, second ... - brave, brave ...
- shovel, rake ... - chair, chair ...
- cubes, pyramid ... - tape recorder, iron ...
- car, bus ... - skirt, trousers ...
- apple, pear ... - cucumber, carrot ...
- chicken, goose ... - cow, sheep ...
Game "Perform the movements"
The goal is to develop attention.
Instruction: Try to perform the movements correctly: if you hear the name of an animal - jump up, if you hear the name of a bird - wave your hands, if you hear the name of a school subject - sit down at the table and put your hands on the table.
Words: ruler, cow, backpack, owl, book, bear, elk, notebook, crow, swallow, pen, fox, dove, wolf, globe, pencil, goat, duck, magpie, pencil case, pig, scissors.
Game "Compare items"
The goal is the development of attention, thinking.
Instruction: Compare items with each other. Tell me how they are similar and how they are different.
Boots and socks
- piano and violin
- kettle and plate
- apple and ball
- girl and doll
- clock and thermometer
- board and glass
"Solution of logical problems"
Purpose: development of logical thinking, the ability to draw conclusions.
Instruction: Listen to the puzzles, think and solve them.
Nine bunnies eat one carrot each. How many carrots does it take to feed all the bunnies?
Two girls played with dolls for two hours. How many hours did each of these girls play?

Lena had four beds with carrots and cabbage in her garden. There were more beds with carrots than with cabbages. How many beds with carrots and how many with cabbage did Lena have in her garden?

The thermometer shows three degrees of frost. How many degrees do two of these thermometers show?

Three girls have hair of different lengths. Marina's is longer than Alena's, Alena's is longer than Natasha's. Which girl has the longest hair and which has the shortest? Show Marina, Alena and Natasha in the picture.

Three brothers - Kolya, Vanya and Tolya - study in different classes. Kolya is older than Vanya, and Vanya is older than Tolya. Which of the children is the youngest and which is the eldest? Show Kolya, Vanya and Tolya in the picture.

Materials taken from the book by I. Svetlova "Lessons for preschoolers. Logic"


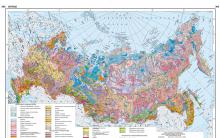




Regional map of the Russian Federation. Map of Russia. Water resources of the country on the map
Large map of the world with countries in full screen
Sun orientation
Map of the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug with cities detailed Map of the railways of the Yamalo Nenets Autonomous Okrug
Where is the Yamal Peninsula located?